Have a question for us? Email us at [email protected]
 | AphidsAphids, also called plant lice, are small (up to ¼ inch), soft bodied insects that will infest most garden plants. Aphids can cause severe distortion and stunting on a plant. |
 | ArmywormsThe armyworm is a sporadic, but occasionally severe pest of turfgrass. They feed as a group, devouring the grass in roughly circular patches before moving on to the next available food. Every bit of green leaf and stem may be stripped by the horde of larvae. |
 | BagwormsBagworms are the larvae of moths. The characteristic brown bags are often seen attached to twigs. The bags are up to two inches long and composed of interwoven bits of dead foliage, twigs and silk. At first it drags the bag around as it feeds on leaves, enlarging the bag as it grows. By late August, the caterpillar finishes its feeding and attaches the bag to a twig. In severe infestations, the entire plant is defoliated and there are bags hanging on many of the twigs. |
 | BillbugsBillbugs are small weevils, 1/3 inch long, with long, downward-pointing snouts and elbowed and clubbed antennae. Often seen walking on paved areas, they first feed on the inside of turfgrass stems and crowns, then move to feed on roots. The affected area appears brown, thin and dead in small irregular spots. |
 | BlightBlight refers to a specific symptom affecting plants in response to infection by a pathogenic organism. It is simply a rapid and complete chlorosis, browning, and then death of plant tissues such as leaves, branches, twigs or floral organs. |
 | Brown PatchBrown Patch initially appears as circular-shaped patches with a diameter of one to five inches. The patches develop quickly up to two feet in diameter and fade to a light brown color. It typically starts to appear during a period of high temperature and high humidity in early summer, and may continue to develop until very late summer. |
 | CankerCankers are a fungus disease caused by a number of different pathogens and attack many varieties of trees. Cankers involve both bark and cambium, girdle twigs and branches causing die back. The fungus may then move down into larger stems and cause perennial cankers possibly girdling the tree trunk causing premature yellowing of leaves, premature leaf drop and possible death. Canker diseases are most often spread in the spring and are most apt to attack those trees and ornamentals growing in infertile soil, weakened by insects and drought, or wounded plants. |
 | Chinch BugsThese very small pests are often associated with open, sunny areas and may be as numerous as 150 to 200 insects per square foot. They actively feed on turfgrass with thick thatch that is exposed to full sunlight during periods of hot, dry weather from early July through late August. |
 | CutwormCutworms are really caterpillars, moth larvae that hide under the soil during the day, coming out in the dark to feed on plants. Typically, they attack the stem of the plant, often of a seedling, consequently cutting it down. |
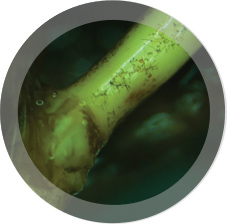 | DeclineTurfgrass decline is a take-all root rot disease. Its initial symptom is a yellow patch ranging from six inches to three feet in diameter. There are no visible lesions on the leaves. A majority of the roots under the patch are lost. The patches may become bare and join together to form larger, irregular-shaped areas. It typically appears in late summer through late fall, especially in the southeastern United States. It is most severe during periods with intense rainfall. |
 | Dollar SpotDollar spot symptoms are typically small, circular, sunken, straw-colored patches of one to two inches in diameter. With severe attacks, the individual spots may join together to form larger, irregular-shaped patches. Lesions may be seen on infected leaves. They typically have a reddish-brown to tan margin and will enlarge across the full width of the leaf blade. Also, multiple lesions may occur on individual blades which cause blighting of the entire leaf. |
 | Fairy RingFairy rings are caused by many different soilin habiting fungi of the class Basidiomycetes. These fungi can cause the development of rings or arcs of deep green grass as well as unthrifty or dead grass. Fairy ring fungi do not attack grass directly, but break down organic matter in the soil. As a result, nitrogen is released which the grass uses, causing it to grow and develop a contrasting green ring. The mushrooms that appear after rainfall are the fruiting bodies of the fungus. |
 | GrubGrubs are the most widespread and destructive pests of turf grasses in the cool -season and transition zones. They damage turf grasses by chewing off the roots near the soil surface. Early symptoms include gradual thinning, yellowing and wilting in spite of adequate soil moisture, as well as the appearance of scattered, irregular dead patches. Infested turf feels spongy underfoot because of the grubs having churned up the underlying soil. |
 | Japanese BeetleJapanese Beetles are small (1/2 inch) metallic green insects with bronze wing covers. The adults feed during the day on a wide variety of plants. They devour flowers, ripening fruit, and tender leaves with small veins, but only eat the tissue between the veins on tree leaves. The adults live for thirty to forty-five days and are most abundant in late July. |
 | Lace BugLace Bugs are small (1/8 inch) insects. The adults have delicate, clear wings that they hold over their bodies. They commonly feed on azaleas, sucking the cell contents from the underside of the leaves, producing a mottling or speckling on the upper surface. There are many species of lace bugs. The most common is the (Stephanitis) on Azaleas and Rhododendrons. |
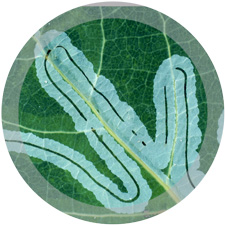 | Leaf MinerA leaf miner is the larva of an insect that lives in and eats the leaf tissue of plants. They feed by creating shallow tunnels, or mines, in young leaves of citrus trees. The damage is unsightly, and if left untreated, can end up causing serious damage to a plant. |
 | Leaf SpotLeaf spot is a common descriptive term applied to a number of diseases affecting the foliage of ornamentals and shade trees. The majority of leaf spots are caused by fungi, but some are caused by bacteria. Leaf spot may result in some defoliation of a plant. |
 | MoleMoles are small grey to black mammals with fine velvety fur. They have hairless snouts and inconspicuous eyes and ears. Their eyesight is poor but they have superior senses of smell, touch and hearing. Their front feet are much larger than their hind feet and have long trowel-like claws used for tunneling in the ground. Moles live in burrows made up of many interconnecting runways that are usually about 6-8 inches underground. |
 | Powdery MildewPowdery mildew is probably the most familiar plant disease. Unlike most other fungus diseases of plants, it grows on the outside of leaves, forming a gray or white “powder”. Also, unlike other fungus diseases, which only infect wet leaves, powdery mildew invades dry leaves as well. |
 | ScaleThere are many different varieties of scale. Scale resembles bumpy bark or fine ash on branches of trees and shrubs. Wherever they feed, they cause a reddening of tissue, usually several times the diameter of the scale. The removal of sap by thousands of scales is what causes the damage. |
 | ShotholeShothole disease starts as brown spots on the leaves. As the leaves expand, the brown areas fall out leaving holes scattered over the leaf surface. |
 | Slime MoldSlime mold is a broad term describing some organisms that use spores to reproduce. They feed on microorganisms that live in any type of dead plant material. They contribute to the decomposition of dead vegetation, and feed on bacteria, yeasts and fungi. |
 | Snow MoldSnow mold is a type of fungus and a turf disease that damages or kills grass after snow melts, typically in late winter. Its damage is usually concentrated in circles three to twelve inches in diameter. |
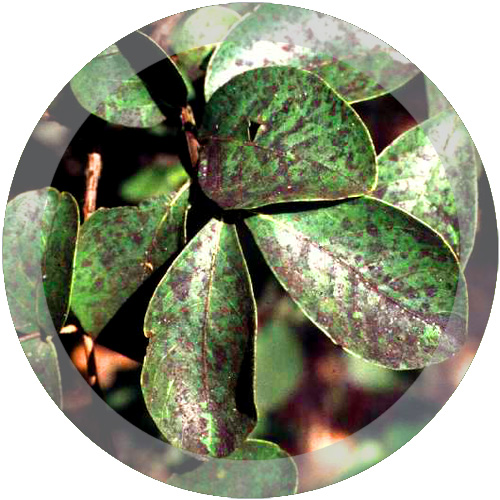 | Sooty MoldSooty mold can be found on a variety of plants. It is caused by any of several fungi that are left on plants by aphids, scale, and other insects that suck sap from the plant. Sooty molds are unsightly, but fairly harmless because they do not attack the leaf directly. |
 | Spider MitesSpider mites are among the most serious pests of ornamental plants. They feed on the underside of the leaves by sucking the juice out of the tissue. Because of the small size and the fact that the suck from the underside of the leaves, they are often overlooked until serious damage occurs. |
 | Spittle BugSpittlebugs cause sporadic damage to warm-season turf grasses. The nymphs feed from inside conspicuous masses of frothy white spittle formed in the turf. Adults are dark colored with two reddish stripes across their back. |
 | WinterkillWinterkill is a general term that is used to define turf loss during the winter. It can be caused by a combination of factors including crown hydration, desiccation, low temperatures, ices sheets and snow mold. |

